Every four years an event takes place that miners and bitcoin enthusiasts wait for: the halving. A protocol included in the bitcoin code, it largely determines the future of the cryptocurrency – and participates in price fluctuations. The next halving will take place in a few weeks.
Many major events take place every four years: whether it is Euro football, leap years, or the Summer Olympics, many fans impatiently await the next edition each time. For miners and cryptocurrency enthusiasts, this is the halving bitcoin — and the next one should take place very soon, in April 2024.
Advertisement
Since the creation of bitcoin in 2008, there have only been 3 halvings, the last having taken place in 2020. Although it is a fairly new practice, halving each time marks the world of cryptocurrencies, and the periods which precede them are an opportunity to speculate and question oneself. Because each halving is an event of particular significance, which reminds us that miners are getting a little closer every day to the end of bitcoins — 90% of all bitcoins have already been mined.
What is bitcoin halving?
Halving, in English, means dividing by two. And that's exactly what's happening.
To “produce” new bitcoins, you have to mine them. To summarize, the miners are put into competition, and must answer equations. The miner who gets there first receives a set number of bitcoins as a reward for their work on the blockchain. This amount was set from the conception of bitcoin by Satoshi Nakamoto, the creator of the cryptocurrency. In the early days of bitcoin, a miner received 50 bitcoins for each new block. This situation has since changed: during the first halving, in 2012, the reward granted to miners increased to 25 bitcoins. In 2016, during the second halving, it increased to 12.5.
Advertisement
Since the last halving of 2020, miners “only” receive 6.25 bitcoins for each new block. During the next halving, which should take place in April 2024, the remuneration will increase to 3,125 bitcoins, and so on.
When will the next bitcoin halving take place? When is the next halving?
The next bitcoin halving will take place in spring 2024, in April. However, there is no precise date yet: the halving takes place every 210,000 blocks. As a block is created approximately every 10 minutes, the duration between each halving fluctuates. It is approximately 4 years, but it is always very difficult to define an exact date in advance. Of course, as the fateful number approaches, it becomes easier to know on what day, and at what time, the halving will take place.
For now, experts have calculated that the next halving should take place in spring 2024, at the beginning of April, but the exact date could still change. Moreover, some sites have different counts: at the time of writing this article, Binance countdown indicates that the halving will take place in 65 days, while that of Bitpanda displays 60 days.
Why does halving exist?
Unlike conventional currency, bitcoin has a fixed number of units: it was decided that there would only be 21 million bitcoins produced. It is this particularity that makes it a rare commodity, like gold: there is a limit. And once it is reached, there will never be another new bitcoin mined.
It is this notion of rarity that gives a product or a metal its value. It is to succeed in giving this aspect to bitcoin that Satoshi Nakamoto decided to establish a limit on bitcoin, to create value. This bitcoin limit has been inserted into the blockchain code, and can never be violated.
It has been calculated that this limit should be reached in 2140, but the exact date when the last bitcoin will be produced has not yet been defined. And with each halving, it will become more difficult to produce a bitcoin, which maintains the longevity of the blockchain — at least until 2140.
Why are there only 21 million Bitcoin?
The sum of 21 million bitcoins was chosen by Satoshi Nakamoto – and he never explained why this number was chosen. However, experts have concluded that there is two very probable hypotheses.
The first assumes that Satoshi Nakamoto chose this number because, in 2009, the total amount of money in circulation in the world was 21 trillion dollars. Hoping that bitcoin one day becomes the base currency for the world, one bitcoin would then have a fixed value, corresponding to 1 million dollars.
The other assumption is based on the time required to mine a block. The parameters of bitcoin today mean that a block is mined approximately every ten minutes, thanks to a protocol that adjusts the difficulty. The number of 21 million would therefore correspond to mathematical logic, applied simply for convenience.
How many bitcoins are in circulation?
For now, a little more than 19 million bitcoins have been mined — there are therefore a little less than 2 million left to be mined in the future. This may not seem like much, but thanks to halving, the remaining 2 million units will take much longer to produce than the 19 million already mined. It has been calculated that the very last bitcoin should be mined in 2140, but the exact date is not yet precisely known.
How does the bitcoin halving take place?
Halving is included in the code. Concretely, halving does not change anything in the production of bitcoin itself. The difference will only be felt by miners who produce the 210,001st and subsequent blocks, who will receive only 3,125 bitcoins as a reward instead of the usual 6.25 bitcoins.
Since halving is included in the bitcoin code, there is nothing special to do or organize: it takes place on its own.
What consequences for bitcoin?
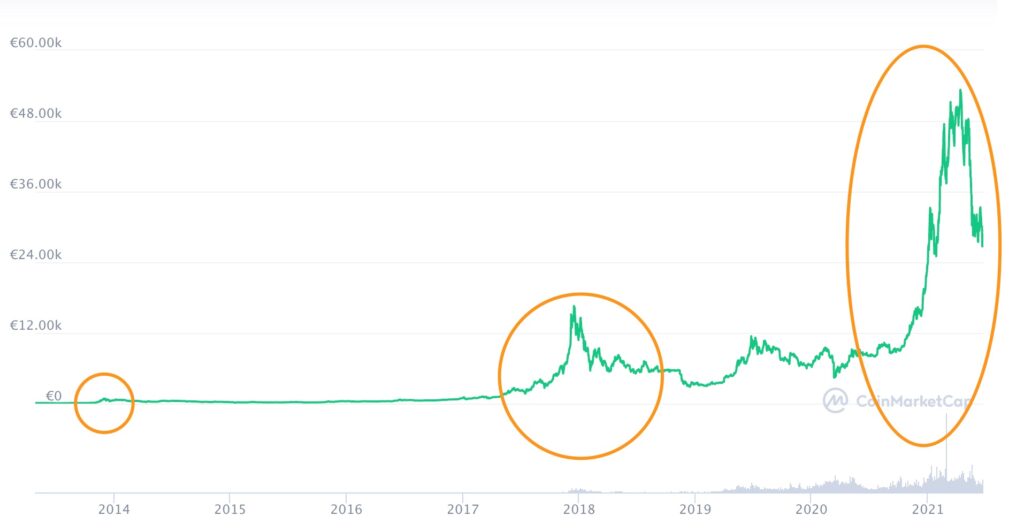
The consequences of the halving on the price of bitcoin are not necessarily felt immediately afterwards, but they are very real. THE specialized site Investopedia explains that halvings have always corresponded to moments of sharp increase in the price of bitcoin. This trend is also quite logical: the number of bitcoins produced is becoming rarer, which only increases its value.
“ The first halving, which took place in November 2012, caused the price of bitcoin to rise from $12 to $1,207 in one year. The second halving occurred in July 2016, when the price stagnated around $650, and a year later, bitcoin experienced its first peak and reached the record price of $16,000. “. And the last halving took place in May 2020, just a few months before bitcoin broke its previous record and rose to more than $63,000.
The next halving
What will happen when there is no more bitcoin?
If the only interest of miners in producing new blocks and ensuring the integrity of the blockchain is to receive remuneration in bitcoin, what will happen when no more bitcoins are produced?
Although this event is not expected before 2140, many people have already looked into the subject, because it is a crucial issue. The solution envisaged, for the moment, is to pay miners to ensure the proper functioning of the blockchain. Like maintenance fees, in a way.
For the moment, minors are already receiving transaction fees each time a transaction is registered on the blockchain. These fees only represent a very small part of their income, but in the future, they could very well represent the entirety, which would certainly inflate prices.
Do other cryptocurrencies have halvings?
What about other cryptocurrencies? The situation is varied.
Ethereum, the second most popular cryptocurrency behind bitcoin, does not have a fixed number of units. For the moment, there is therefore no real need to introduce a halving – but this also means that the rewards for miners fluctuate. Their value generally varies between 2 ETH and 2.5 ETH, But this has not always been the case. Until 2018, the creation of a block was rewarded with 3 ETH, before miners do not decide to lower voluntarily the remuneration – in order to increase the price of ethereum. Since then, on the platform Ethereum Improvment Proposalsone user even suggested gradually lowering the price to 1 ETH.
But other cryptocurrencies have a fixed number of units. For Monero, the limit is set at 18.9 million, and the currency has implemented a system of gradual reduction in remuneration over time – a less abrupt change than that of bitcoin.
